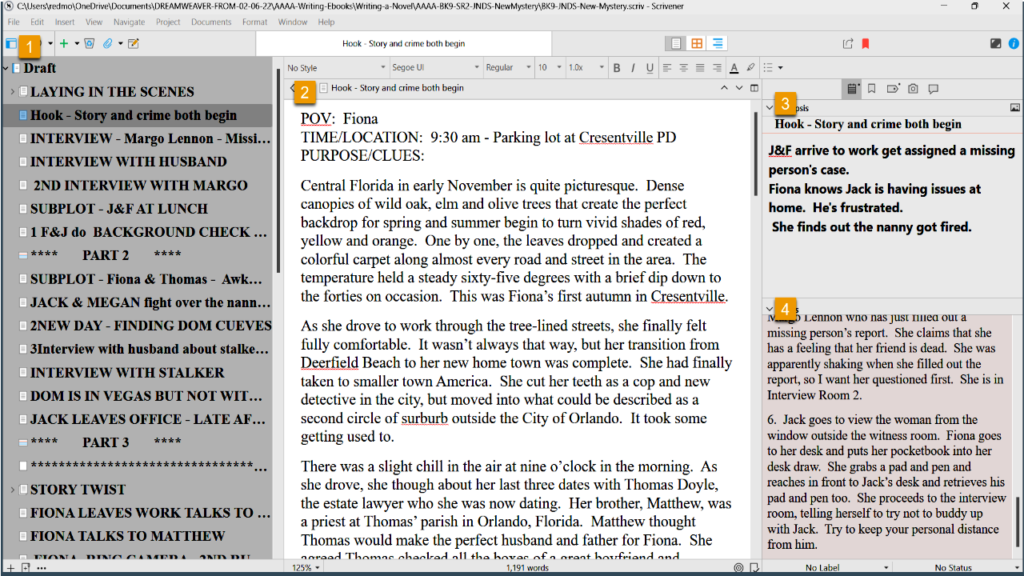
HOW TO VS. WORK FLOW DEMONSTRATION:
 There are many blog posts and videos on the internet about how to write a novel. Much of the advice is general in nature and only broad-stroke tips. This video seeks to go one step further and open my last book, which is still being proofread in Layer 8, and show a work-flow demonstration.
There are many blog posts and videos on the internet about how to write a novel. Much of the advice is general in nature and only broad-stroke tips. This video seeks to go one step further and open my last book, which is still being proofread in Layer 8, and show a work-flow demonstration.
WRITING TIPS AS AN APPLIED SCIENCE:
Many of the tips that I came upon when I first started writing were great but I didn't know how to apply them. Many techniques require a second phase of 'how to apply this advice'. This is most times missing from the how-to blogs and videos.
THIS IS THE VIDEO I WISH I HAD WHEN I STARTED WRITING:
I am not holding myself out as an authority on writing or even writing techniques. The purpose of this video is to show one work flow that other newbie writers can see that will hopefully help them see the theories in these how-to videos and blog posts in action. That's my purpose here.
WRITING IN 8 LAYERS:
 I am in the process of finishing my 14th novel. I started out like many of you as a self-taught author who took in unorganized, uncurricularized information and had to make sense of it all. I devised this 8 Layer system to try to write a novel as efficiently as was possible. I offer it to you for whatever weight you wish to give it.
I am in the process of finishing my 14th novel. I started out like many of you as a self-taught author who took in unorganized, uncurricularized information and had to make sense of it all. I devised this 8 Layer system to try to write a novel as efficiently as was possible. I offer it to you for whatever weight you wish to give it.
VIDEO 1 - Layers 1 to 6
In Video 1, I go into the process of coming up with a broad-stroke storyline that you know you can use as a story spine. Presently I use FreeMind.com software; it's free and it's easy to use. I go into a little detail about this, but I have other blog posts and videos on my YouTube Channel where I go into more depth about how I do this.
Then I go into Scrivener for Layer 2 through Layer 6. I demonstration what happens in each layer and I try to give beginner tips in each layer to further help the newbie.
VIDEO 2 - Layers 7 & 8 - in Microsoft Word
In the second video, I go into Microsoft Word and complete Layers 7 and 8. I believe by seeing this behind-the-scenes look at a real novel, it will encourage newbies who may be struggling with the actual work flow of writing a novel. I hope you enjoy it.
Be sure to join my newsletter for book promotions, free books, movie reviews from a writer's perspective and some other goodies I will share along the way.

 In a mystery, crime novel, or thriller, the clues and their revelations need to be planned so the story clues can remain disjointed in the beginning, but then slowly come together like a jigsaw puzzle. This keeps the reader guessing -- which is part of the mystery readers' enjoyment.
In a mystery, crime novel, or thriller, the clues and their revelations need to be planned so the story clues can remain disjointed in the beginning, but then slowly come together like a jigsaw puzzle. This keeps the reader guessing -- which is part of the mystery readers' enjoyment.
 1. Who is the Ghost? Why has the Ghost arisen? Why is the Person not Resting in Peace? What is the Ghost's purpose for appearing? This is the backstory that will be dropped like breadcrumbs throughout the storyline. (Ghost-Story.png)
1. Who is the Ghost? Why has the Ghost arisen? Why is the Person not Resting in Peace? What is the Ghost's purpose for appearing? This is the backstory that will be dropped like breadcrumbs throughout the storyline. (Ghost-Story.png) 1. What is it about the house that's creepy?
1. What is it about the house that's creepy?
 It may help to think of yourself as more of a Town Crier.
It may help to think of yourself as more of a Town Crier. 1. Using the read aloud feature in Microsoft Word, I read the book aloud as I read along with it. This gives you an idea of how the book will sound in the reader's mind.
1. Using the read aloud feature in Microsoft Word, I read the book aloud as I read along with it. This gives you an idea of how the book will sound in the reader's mind. Most of these mistakes were ones that were not even on my radar at the time they were made.
Most of these mistakes were ones that were not even on my radar at the time they were made. When I first got the idea of writing a novel, I did research for about a year. I read several how to books on every subject under the title of writing a novel and self-publishing. (Cat on book shelf)
When I first got the idea of writing a novel, I did research for about a year. I read several how to books on every subject under the title of writing a novel and self-publishing. (Cat on book shelf) So above is a list of the chronology I pieced together as being the proper chronological list of how to write and publish a book:
So above is a list of the chronology I pieced together as being the proper chronological list of how to write and publish a book: Beta Readers often times read books very early in the process -- before the book is even finished to give early feedback. This is a great idea if you're not sure about your characters or if the plot is good enough, etc. Let's face it, in the beginning it's hard to think you're book is a masterpiece when it's your first one -- at least it was for me. There is a definite high-level purpose in having Beta Readers. They are worth their weight in gold.
Beta Readers often times read books very early in the process -- before the book is even finished to give early feedback. This is a great idea if you're not sure about your characters or if the plot is good enough, etc. Let's face it, in the beginning it's hard to think you're book is a masterpiece when it's your first one -- at least it was for me. There is a definite high-level purpose in having Beta Readers. They are worth their weight in gold. However, here is where I made the terrible mistake and found out the hard way about this particular landmine: I offered my Vampire book Darius - A Vampire Story as a beta book but it had not been finalized, professionally edited or proofread. Now, in the ad copy for the link to download, I clearly posted it as a beta copy that had not been edited, etc. However, once a book is downloaded to an eReader, no one will remember this book is only a beta copy. And the second mistake I made here was that I didn't put anything in the book itself.
However, here is where I made the terrible mistake and found out the hard way about this particular landmine: I offered my Vampire book Darius - A Vampire Story as a beta book but it had not been finalized, professionally edited or proofread. Now, in the ad copy for the link to download, I clearly posted it as a beta copy that had not been edited, etc. However, once a book is downloaded to an eReader, no one will remember this book is only a beta copy. And the second mistake I made here was that I didn't put anything in the book itself. The first time this happened, I just thought the reader was a bit crazy. But after this happened several times, it was only then that I realized that I had released hundreds of beta copies that now lived on people's eReaders. And for some reason, there are a lot of readers who take typos or grammar errors personally. It seems to trigger them and their reviews are more like rants.
The first time this happened, I just thought the reader was a bit crazy. But after this happened several times, it was only then that I realized that I had released hundreds of beta copies that now lived on people's eReaders. And for some reason, there are a lot of readers who take typos or grammar errors personally. It seems to trigger them and their reviews are more like rants.
 GoodReads is probably the largest single pool of avid readers and book lovers out there. But goodreads can be a tough crowd for new writers. This is where Darius's bullying started. If I had to do things over again, I would not have focused on Goodreads as a first place to release my books -- even after they were fully edited and proofread. Unfortunately, many of the videos I watched during that first year, talked about how great goodreads was helpful to find beta readers and arc readers and launch a book.
GoodReads is probably the largest single pool of avid readers and book lovers out there. But goodreads can be a tough crowd for new writers. This is where Darius's bullying started. If I had to do things over again, I would not have focused on Goodreads as a first place to release my books -- even after they were fully edited and proofread. Unfortunately, many of the videos I watched during that first year, talked about how great goodreads was helpful to find beta readers and arc readers and launch a book. I didn't realize that the categories on Amazon have a hierarchy to them. It may have been because we were originally allowed to put each book into 10 categories. I had watched a video by
I didn't realize that the categories on Amazon have a hierarchy to them. It may have been because we were originally allowed to put each book into 10 categories. I had watched a video by  So the time to think about the categories is before you even plot out or write the book. Once you have a plot idea, that's the time to look at the categories and think about where the book would fit, and what you can tweak about the storyline to fit into a sub category or a less competitive category? Can you make the story happen in the west to be a Western Romance? Can you put the story into olden times to make it a historical novel, ore even better, put it in a specific time period? The time to think about categories is right after you have know you have a workable plotline.
So the time to think about the categories is before you even plot out or write the book. Once you have a plot idea, that's the time to look at the categories and think about where the book would fit, and what you can tweak about the storyline to fit into a sub category or a less competitive category? Can you make the story happen in the west to be a Western Romance? Can you put the story into olden times to make it a historical novel, ore even better, put it in a specific time period? The time to think about categories is right after you have know you have a workable plotline. Mistake Number five requires a little explanation. My inspiration for my vampire series was the old Dark Shadows Soap Opera from the late '60s and early '70s. I never watched it as a kid but everyone I knew did. I didn't watch it because I had to walk too far to get home from school in time. This vampire series, like most soap operas at that time, was melodramatic and being a gothic and supernatural story, the storylines were completely crazy. But I loved the show anyway.
Mistake Number five requires a little explanation. My inspiration for my vampire series was the old Dark Shadows Soap Opera from the late '60s and early '70s. I never watched it as a kid but everyone I knew did. I didn't watch it because I had to walk too far to get home from school in time. This vampire series, like most soap operas at that time, was melodramatic and being a gothic and supernatural story, the storylines were completely crazy. But I loved the show anyway. So, with limited knowledge of the whole vampire genre, I went on to write a vampire book series. My vampire owns and operates a funeral home and keeps a bevy of 3 women to supply the blood he needs. He normally picks up runaways from the train and bus stations, but he winds up falling in love with the daughter of a wealthy, influential family in Newport Rhode Island. There is also a monastery of monks that live on the opposite side of the cemetery that Darius also owns.
So, with limited knowledge of the whole vampire genre, I went on to write a vampire book series. My vampire owns and operates a funeral home and keeps a bevy of 3 women to supply the blood he needs. He normally picks up runaways from the train and bus stations, but he winds up falling in love with the daughter of a wealthy, influential family in Newport Rhode Island. There is also a monastery of monks that live on the opposite side of the cemetery that Darius also owns. So how does all this fit into mistake number 5? Well, there's no category for tongue-in-cheek vampire stories. Also, fifty years have passed since this show ended and a lot has happened to the vampire genre in that time. First there was Anne Rice and her books and subsequent movies which are all dead serious and there's no tongue in cheek humor of any kind. I only read the first book and it was steeped in darkness and despair. Because I read for enjoyment, the level of despair was too much for me so I never read the other books.
So how does all this fit into mistake number 5? Well, there's no category for tongue-in-cheek vampire stories. Also, fifty years have passed since this show ended and a lot has happened to the vampire genre in that time. First there was Anne Rice and her books and subsequent movies which are all dead serious and there's no tongue in cheek humor of any kind. I only read the first book and it was steeped in darkness and despair. Because I read for enjoyment, the level of despair was too much for me so I never read the other books.



 Turning the viewing of a movie into a writing exercise will change the way in which you watch the movie. For your spouse, it won't change anything. Most people love to go into the story not knowing anything. There are some who any hint of a spoiler will ruin the movie for them. You may be one of them now!
Turning the viewing of a movie into a writing exercise will change the way in which you watch the movie. For your spouse, it won't change anything. Most people love to go into the story not knowing anything. There are some who any hint of a spoiler will ruin the movie for them. You may be one of them now! Find a summary of the movie on Wikipedia. Most movies have a page about them and it gives all the technical information about who wrote the original story, the producer, director, stars, etc. But there is a section entitled PLOT. This is where the plot is laid out for you.
Find a summary of the movie on Wikipedia. Most movies have a page about them and it gives all the technical information about who wrote the original story, the producer, director, stars, etc. But there is a section entitled PLOT. This is where the plot is laid out for you. To be honest, most plots are too long to even remember or put together with one reading. I can usually follow the plotline for about the first four paragraphs. After that, I can't remember who is who but it doesn't matter. As long as you have a gist of an idea of what will take place, it allows you to watch for it.
To be honest, most plots are too long to even remember or put together with one reading. I can usually follow the plotline for about the first four paragraphs. After that, I can't remember who is who but it doesn't matter. As long as you have a gist of an idea of what will take place, it allows you to watch for it.

 THIRD: Classic films relied more on dialogue, staging and backdrops to tell the story. This is the richness that I find most helpful to see and learn from as an author. Modern storytelling is worried about the 3-second attention span. Older movies assumed the audience was grown up and could sit still and pay attention for a few minutes without intense stimulation.
THIRD: Classic films relied more on dialogue, staging and backdrops to tell the story. This is the richness that I find most helpful to see and learn from as an author. Modern storytelling is worried about the 3-second attention span. Older movies assumed the audience was grown up and could sit still and pay attention for a few minutes without intense stimulation. FIFTH: Newer movies have upgraded post production technology and CGI, so they are now focused on movie effects, jump scares and gore shocks. Although many of you may enjoy this type of thing, it really doesn't have much to teach a new author.
FIFTH: Newer movies have upgraded post production technology and CGI, so they are now focused on movie effects, jump scares and gore shocks. Although many of you may enjoy this type of thing, it really doesn't have much to teach a new author. Everyone has to find their own subgenres whether it be old gothic movies or old mystery movies. But a good place to start is at Wikipedia. Below are two links to the 1960s and 1970s in film. Movies made in these years would fall into the categories I mentioned above.
Everyone has to find their own subgenres whether it be old gothic movies or old mystery movies. But a good place to start is at Wikipedia. Below are two links to the 1960s and 1970s in film. Movies made in these years would fall into the categories I mentioned above. If you are watching the movie on a computer, take a screen shot of a scene and then set up an imaginary happenstance that occurs in this setting. Describe the setting in words, attempting to capture the essence of what you saw on film. Doing this a few times will help you get better and better in describing backgrounds and scene settings.
If you are watching the movie on a computer, take a screen shot of a scene and then set up an imaginary happenstance that occurs in this setting. Describe the setting in words, attempting to capture the essence of what you saw on film. Doing this a few times will help you get better and better in describing backgrounds and scene settings.


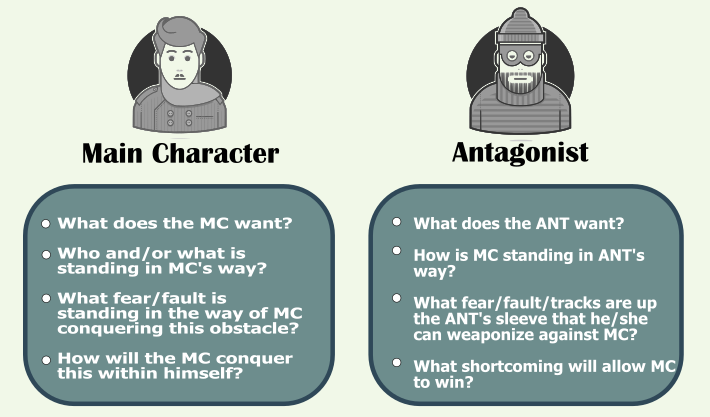
 I use a four-part plot structure, so I break my character arc into four sections. This allows me to keep up with the character development and also don’t resolve the inner conflict too early.
I use a four-part plot structure, so I break my character arc into four sections. This allows me to keep up with the character development and also don’t resolve the inner conflict too early.



 If you are stumped for a main story, or if you are stumped for what happens now, or even if you have written yourself into a bit of a corner, this instructional will help, along with your own creativity and thinking, to bring about new possibilities.
If you are stumped for a main story, or if you are stumped for what happens now, or even if you have written yourself into a bit of a corner, this instructional will help, along with your own creativity and thinking, to bring about new possibilities. 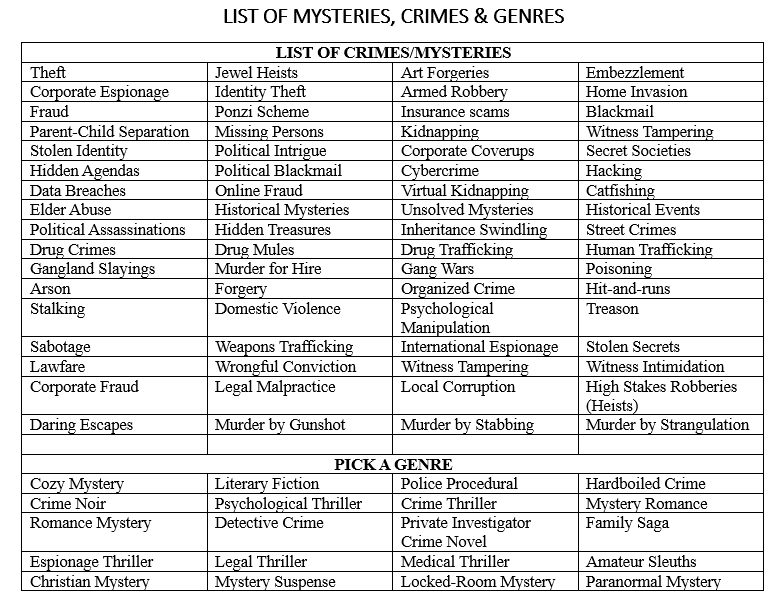

 Once you have a perpetrator and the cast of necessary characters, then it’s time to answer the following questions:
Once you have a perpetrator and the cast of necessary characters, then it’s time to answer the following questions:
 Before you exert too much energy fleshing out any character or story details, be sure to check to make sure you can design a three-prong storyline out of this budding storyline. One prong will be a red herring storyline, someone who may look guilty, but is exonerated in the middle or end of the story. The second prong is a second suspect or a wrong suspect who will look guilty for a large segment of the storyline. And the final prong will be for the real culprit. In order to have a story that works, you will need a believable crime that can meld these three prongs into one suspenseful story.
Before you exert too much energy fleshing out any character or story details, be sure to check to make sure you can design a three-prong storyline out of this budding storyline. One prong will be a red herring storyline, someone who may look guilty, but is exonerated in the middle or end of the story. The second prong is a second suspect or a wrong suspect who will look guilty for a large segment of the storyline. And the final prong will be for the real culprit. In order to have a story that works, you will need a believable crime that can meld these three prongs into one suspenseful story. As you use this worksheet and these techniques, a crime skeleton will emerge. Some attempts at this will go flat in the early stages for any number of reasons. But some storylines will begin to almost shape themselves.
As you use this worksheet and these techniques, a crime skeleton will emerge. Some attempts at this will go flat in the early stages for any number of reasons. But some storylines will begin to almost shape themselves. Pulp Fiction become popular during the depression of the 1920s and 1930s. Publishers at the time used a very cheap “pulp” paper in order to produce these short stories and magazines that cost about a quarter. Yes, twenty-five cents!
Pulp Fiction become popular during the depression of the 1920s and 1930s. Publishers at the time used a very cheap “pulp” paper in order to produce these short stories and magazines that cost about a quarter. Yes, twenty-five cents!

 This book is for beginners who are publishing their first or second novel and they are still a little skittish about what else goes into a book. I’ll lay it out so you can easily follow the list and be confident that you’re not forgetting anything. These page suggestions are taken from the publishing industry. These are the pages that appear in a book published by a publishing house.
This book is for beginners who are publishing their first or second novel and they are still a little skittish about what else goes into a book. I’ll lay it out so you can easily follow the list and be confident that you’re not forgetting anything. These page suggestions are taken from the publishing industry. These are the pages that appear in a book published by a publishing house. Writing a novel is a huge undertaking. There are many things that go into the writing of a fiction story. The best tip I can pass on is this: Break everything down into little bite-sized pieces. By doing this, you can reduce a huge project down to do-able portions that can be done whether you have 2 hours a week to write or two full days! It only requires a little planning and organization.
Writing a novel is a huge undertaking. There are many things that go into the writing of a fiction story. The best tip I can pass on is this: Break everything down into little bite-sized pieces. By doing this, you can reduce a huge project down to do-able portions that can be done whether you have 2 hours a week to write or two full days! It only requires a little planning and organization. It’s important to keep reading as your own journey as a writer continues. Each author has a different style and uses different storytelling techniques. The stories don’t even have to be great. You can learn from the good, the bad and the bland. Just analyzing what made a book bland is a great lesson in itself. Did the story need more action? Did the story get stuck somewhere?
It’s important to keep reading as your own journey as a writer continues. Each author has a different style and uses different storytelling techniques. The stories don’t even have to be great. You can learn from the good, the bad and the bland. Just analyzing what made a book bland is a great lesson in itself. Did the story need more action? Did the story get stuck somewhere?  or other books you read. Reading other authors is crucial no matter where you are on the writing spectrum. However, when you’re new, you can learn a lot from watching mystery or crime noir movies. I like movies from the 1940s, 1950s, and 1960s. The movies in these decades didn’t have CGI and the directors had to use the stage to tell the story. They used wider shots and props to assist the storytelling. By watching these older movies, you can learn a lot regarding writing.
or other books you read. Reading other authors is crucial no matter where you are on the writing spectrum. However, when you’re new, you can learn a lot from watching mystery or crime noir movies. I like movies from the 1940s, 1950s, and 1960s. The movies in these decades didn’t have CGI and the directors had to use the stage to tell the story. They used wider shots and props to assist the storytelling. By watching these older movies, you can learn a lot regarding writing.  It’s a good idea to read the synopsis before you view the movie. Knowing at least a basic outline of the story will allow you to absorb more as an author. If you go into the movie blindly, you will be “experiencing the movie” as a viewer only. By knowing ahead of time what story will be unfolding, it will allow you to watch specifically for certain scenes to unfold. You can watch what tools are used to move the story along.
It’s a good idea to read the synopsis before you view the movie. Knowing at least a basic outline of the story will allow you to absorb more as an author. If you go into the movie blindly, you will be “experiencing the movie” as a viewer only. By knowing ahead of time what story will be unfolding, it will allow you to watch specifically for certain scenes to unfold. You can watch what tools are used to move the story along. 
 If you are looking for a suggestion, I would suggest Rebecca for the first movie. This movie was directed by Alfred Hitchcock and it has a lot of gothic atmosphere. There is also a psychological plotline in this story so it is a goldmine for learning storytelling tools.
If you are looking for a suggestion, I would suggest Rebecca for the first movie. This movie was directed by Alfred Hitchcock and it has a lot of gothic atmosphere. There is also a psychological plotline in this story so it is a goldmine for learning storytelling tools.