 This blog post will be a peek behind the author workflow in Layer 5 of my Novel Writing in Layers Series. I am writing Book 6, Majestic Landings, in my police procedural series, Jack Nolan Detective Series.
This blog post will be a peek behind the author workflow in Layer 5 of my Novel Writing in Layers Series. I am writing Book 6, Majestic Landings, in my police procedural series, Jack Nolan Detective Series.
Let me set the table, so to speak, about where I am in the book right now. I just finished Layer 4 which is the Down and Dirty First Draft, which I believe is the hardest layer to write.
BEGINNING LAYER 5
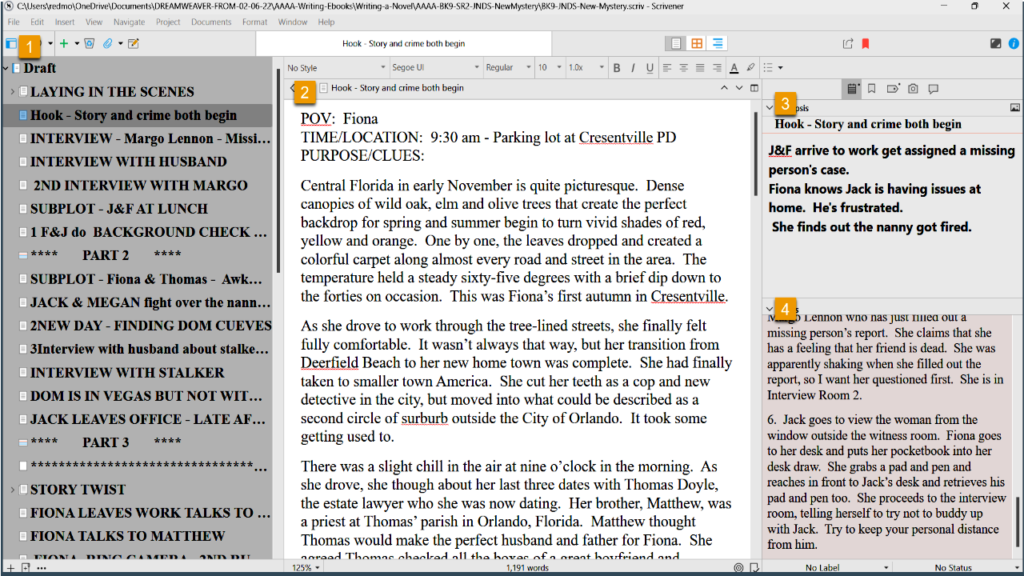
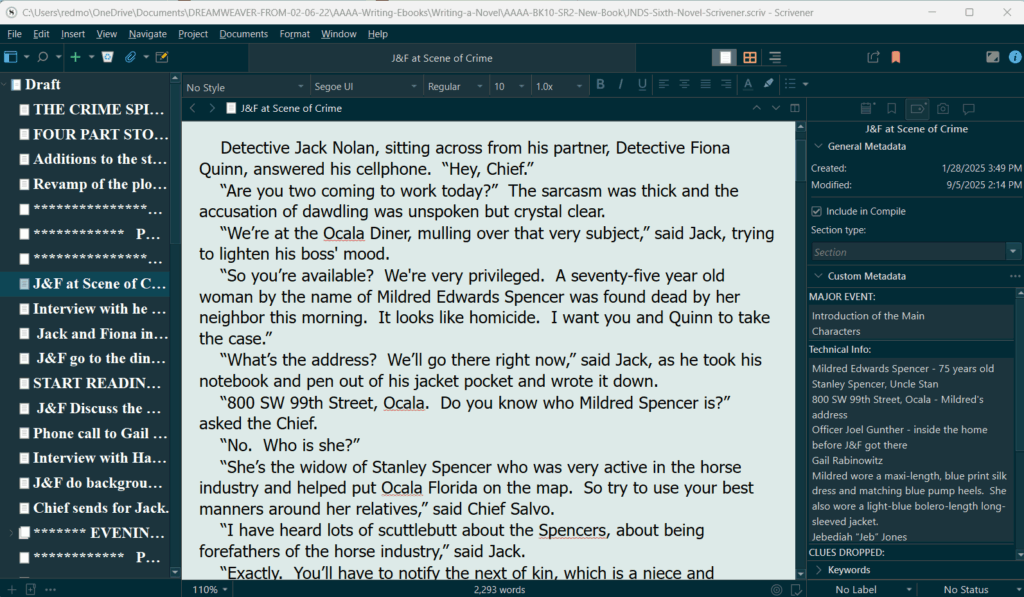 Above is a snapshot of the book as it now exists in Scrivener, which is the program I write Layers 1 to 6 in. I have gone ahead and filled in a few of the scenes so that I can explain to you what I do in Layer 5.
Above is a snapshot of the book as it now exists in Scrivener, which is the program I write Layers 1 to 6 in. I have gone ahead and filled in a few of the scenes so that I can explain to you what I do in Layer 5.
ON THE LEFT SIDE IS THE BINDER: The top folder is called draft, which is a default in Scrivener. Each sub-document is one scene in the novel. I also add in a few blank documents between Parts 1, 2, 3 and 4, so I can see how the story action is balancing inside the plot structure.
IN THE CENTER PANEL: This is where I write the scenes.
ON THE RIGHT SIDE IS THE INSPECTOR WINDOW: This section allows you to add a scene synopsis on another tab, but above, I have captured what it looks like on the Metadata Section.
WHAT HAPPENS IN LAYER 5?
This is my first layer of proofreading. I only focus on the following things in this layer of writing.
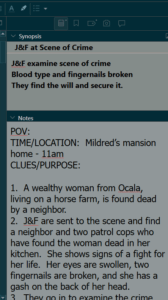 1. Making sure the scenes line up and flow smoothing and fill in the Synopsis box if I forgot to do it in Layer 4. I have a snapshot of the Synopsis box to the right or below. This allows me to look at my work in the Outline Mode where I can see the novel from a bird's eye view.
1. Making sure the scenes line up and flow smoothing and fill in the Synopsis box if I forgot to do it in Layer 4. I have a snapshot of the Synopsis box to the right or below. This allows me to look at my work in the Outline Mode where I can see the novel from a bird's eye view.
Since it's in the photograph here, I will also mention that I copy my scene outlines and paste them into the Notes section in case I want to review them.
2. I enter all of the character descriptions and location descriptions in this layer too.
3. I also check on the crime and investigation timeline as well as the novel timeline.
3A: The crime timeline I track with the metadata, which I will mention again below. I also use the Scrivener Highlighter to set off anything that references the crime timeline. This way, towards the end of this layer, if I decided to tighten up the timeline or find out I need a little extra time, it is very easy to quickly scroll through the novel and find any references to the timeline easily.
 3B: All novels have a timeline too. A crime novel is usually a day to several weeks; whereas Gone with the Wind cover years and years. In each scene, I start with a little template referencing the point of view, the time/location and the clues/purpose.
3B: All novels have a timeline too. A crime novel is usually a day to several weeks; whereas Gone with the Wind cover years and years. In each scene, I start with a little template referencing the point of view, the time/location and the clues/purpose.
As stated above, I read through the scenes, making sure that the last scene flows into the next scene. For example: If my detectives 'get into the car to return to the station,' I make sure I'm not referencing where they were before they got into the car, and stating again that they are entering the car.
I also watch my novel timeline to make sure the timing in the day is lining up with what's possible for human beings. In my humble opinion, authors have a lot of leeway to stretch the day, if needed, but if we go overboard, at some point, it pulls the reader's mind out of the book when they realize there's too much activity for one day as humans. By keeping an eye on the novel timeline, this prevents me from stretching a little too much.
THE METADATA - HOW AND WHY TO ADD CUSTOM META DATA.
 Some authors probably don't use the metadata section and that's fine. But I like to look at the novel in the Outline Mode and this is where the custom metadata comes into play.
Some authors probably don't use the metadata section and that's fine. But I like to look at the novel in the Outline Mode and this is where the custom metadata comes into play.
Every novel is different, so I am focusing on different things in each one. In this novel, there are multiple suspects, all of whom have shaky alibis, so the crime timeline and some other things are very important. So in this novel, I created metadata sections as follows:
- Major Event - What happens in the scene
- Technical information - Names, addresses, where body was found, first witness, etc.
- Clues dropped - Chronological list of clues that drop
- Time Line of the Crime - Time of death, time body was found, etc.
- Relationships - Romantic Subplot and Character Arcs
WHAT'S NEXT IN LAYER 5?
Once I proofread all the way through, add in the descriptions, and my meta data, then I want to look at certain things to check on myself. I can set up the Outline Mode so I can see the Synopsis, the Clues, and the Crime Timeline side by side. I will post a picture below.
I can then look closely to make sure I don't mention a lab report that hasn't been delivered. Or one of the suspects is mentioned before anyone points them out, things like this.
I can see the chronology of the clues that have dropped to make sure that they are chronologically correct. I'm sure you get the drift.
My color scheme in Scrivener may make some of these things hard to see, so I have posted the Custom Metadata diagram below so you can see where things go and what the icons look like.
 After looking at the various meta data in this bird's eye view setup, I'm ready to enter Layer 6, which is another round of proofreading; and again, I only focus on a few things.
After looking at the various meta data in this bird's eye view setup, I'm ready to enter Layer 6, which is another round of proofreading; and again, I only focus on a few things.
I have done a short video about this in case you want to see me go over it inside Scrivener. There is a bit more information here for beginners, but it's good to watch it live too.
Be sure to check back to see another Live Peek Behind Layer 6! Be aware that I am not proclaiming myself as an expert novelist or the knower of all things. However, I used to search all the time for authors' workflow, but nothing ever showed up. I believe I could have advanced a lot faster if I had tips from more season's authors and that's my purpose here.
By seeing how one author does things, you may only take away one tip that will help you in the system you already use. I hope this blog post helps!






 Every writer has strengths and weaknesses. At some point, it's important for each writer to recognize what their particular weaknesses are.
Every writer has strengths and weaknesses. At some point, it's important for each writer to recognize what their particular weaknesses are. Once I'm done with that list, I search through the document using the Control F (Find feature) to check that all of my quotes have an open quotation mark and a close quotation mark. It takes a little time to do this, but I feel much more secure when I check them. I ALWAYS find an extra one or a couple of missing quotation marks.
Once I'm done with that list, I search through the document using the Control F (Find feature) to check that all of my quotes have an open quotation mark and a close quotation mark. It takes a little time to do this, but I feel much more secure when I check them. I ALWAYS find an extra one or a couple of missing quotation marks. Now, some of you may say, why bother if you're just going to hand over the manuscript to an editor?
Now, some of you may say, why bother if you're just going to hand over the manuscript to an editor?
 Once you have all of these story parts connected, this is the easiest time to take the characters from stick figures into two-dimensional characters. The characters will be transformed into their final three-dimensional states during the actual book-writing process, so the goal in this brainstorming process is to sculpt two-dimensional characters.
Once you have all of these story parts connected, this is the easiest time to take the characters from stick figures into two-dimensional characters. The characters will be transformed into their final three-dimensional states during the actual book-writing process, so the goal in this brainstorming process is to sculpt two-dimensional characters. So the next set of questions is designed to take your story idea from this crime/mystery spine to a second dimensional level. This is the point where you can add realistic character traits and motivations that will fit inside the plotline. I assure you, there won't be any more trying to fit a fully-fleshed out round character into a square plotline. This process will avoid that.
So the next set of questions is designed to take your story idea from this crime/mystery spine to a second dimensional level. This is the point where you can add realistic character traits and motivations that will fit inside the plotline. I assure you, there won't be any more trying to fit a fully-fleshed out round character into a square plotline. This process will avoid that.
 Unless you are writing in a series where the main character is already fully developed, it's best to wait until after choosing the antagonist, suspects, and motivations for each of them to infuse the main protagonist with human traits. Why? Because the protagonist will need to have a character arc and this will need to be developed over the action of the story and in relation to all of the different suspects.
Unless you are writing in a series where the main character is already fully developed, it's best to wait until after choosing the antagonist, suspects, and motivations for each of them to infuse the main protagonist with human traits. Why? Because the protagonist will need to have a character arc and this will need to be developed over the action of the story and in relation to all of the different suspects. Once you know who, what, when, where and how the story will proceed, now you can choose the type of protagonist needed to solve the mysteries. Now it is time to sketch in more character traits and details. This process will take your stick figure and raise it to a level of a two-dimensional character.
Once you know who, what, when, where and how the story will proceed, now you can choose the type of protagonist needed to solve the mysteries. Now it is time to sketch in more character traits and details. This process will take your stick figure and raise it to a level of a two-dimensional character. What fears or human frailty will the sleuth need to overcome in solving the crime? This is what drives a character arc. What will the main character ultimately learn? Does he have a fear of heights? Is she normally timid and now has to be courageous? What inner fears will be challenged when going about solving the crime and/or mystery?
What fears or human frailty will the sleuth need to overcome in solving the crime? This is what drives a character arc. What will the main character ultimately learn? Does he have a fear of heights? Is she normally timid and now has to be courageous? What inner fears will be challenged when going about solving the crime and/or mystery?
 Again, it's easier to create a character after you already know what he/she will be required to do physically, what skills they will need, and what human flaw can make this challenging. It's easier than forming a main character that you like and then trying to fit him or her into a storyline that already has a life of its own.
Again, it's easier to create a character after you already know what he/she will be required to do physically, what skills they will need, and what human flaw can make this challenging. It's easier than forming a main character that you like and then trying to fit him or her into a storyline that already has a life of its own. Is there a moral dimension to the conflict that raise the stakes? Does the protagonist's decision have far-reaching ethical implications? Is he/she fighting for justice, truth, or a greater good? Moral dilemmas add weight and complexity to the stakes.
Is there a moral dimension to the conflict that raise the stakes? Does the protagonist's decision have far-reaching ethical implications? Is he/she fighting for justice, truth, or a greater good? Moral dilemmas add weight and complexity to the stakes. Is there a ticking clock in your storyline? Is there a deadline to solve the crime? Is there a rapidly-approaching event that can significantly heighten the stakes? The faster the clock ticks, the more intense the pressure, the higher the stakes. This added time pressure can turn a mystery into a thriller.
Is there a ticking clock in your storyline? Is there a deadline to solve the crime? Is there a rapidly-approaching event that can significantly heighten the stakes? The faster the clock ticks, the more intense the pressure, the higher the stakes. This added time pressure can turn a mystery into a thriller.
 When Brainstorming a Novel Storyline, what questions do you need to ask and answer? After having written 14 novels, I believe this technique that I'm about to tell you about will help anyone brainstorm a working plotline.
When Brainstorming a Novel Storyline, what questions do you need to ask and answer? After having written 14 novels, I believe this technique that I'm about to tell you about will help anyone brainstorm a working plotline. What will the mystery or crime in the novel be? Will it be a psychological thriller and mind control is the crime? Will it be a murder mystery? If so, what is the cause of death? If it's a science fiction plotline, what mystery will hook the reader and thread through the entire story only to be revealed at the end?
What will the mystery or crime in the novel be? Will it be a psychological thriller and mind control is the crime? Will it be a murder mystery? If so, what is the cause of death? If it's a science fiction plotline, what mystery will hook the reader and thread through the entire story only to be revealed at the end? The type of crime or mystery will dictate the investigation methods and details. It will also dictate what clues will be needed in order to slowly reveal the mystery throughout the four-part plot structure.
The type of crime or mystery will dictate the investigation methods and details. It will also dictate what clues will be needed in order to slowly reveal the mystery throughout the four-part plot structure. Is he/she a private detective, an amateur sleuth, a police officer, or maybe just a weekend visitor who is inadvertently led into solving a mystery?
Is he/she a private detective, an amateur sleuth, a police officer, or maybe just a weekend visitor who is inadvertently led into solving a mystery? Determine the identity, background, and significance of the victim. This decision can affect the motive, the suspects, and the overall narrative story arc. The victim's characteristics can also influence how the crime impacts other characters or the community at large. Before figuring out who the suspects are, you need to know who the victim is and why they were murdered or wronged in some way. If it's not a crime story but just a mystery or thriller, you will still need a victim. They may not die in the story, but there will be at least an injustice done to them. What is that injustice and who is the victim of it?
Determine the identity, background, and significance of the victim. This decision can affect the motive, the suspects, and the overall narrative story arc. The victim's characteristics can also influence how the crime impacts other characters or the community at large. Before figuring out who the suspects are, you need to know who the victim is and why they were murdered or wronged in some way. If it's not a crime story but just a mystery or thriller, you will still need a victim. They may not die in the story, but there will be at least an injustice done to them. What is that injustice and who is the victim of it? The victim's background, their relationships, and their secrets are all vital. Were they likeable? Did they have known enemies? A compelling victim, even if flawed, gives the reader someone to care about and root for. Even if the victim hasn't been killed or murdered, who is being bullied or targeted as the victim and why?
The victim's background, their relationships, and their secrets are all vital. Were they likeable? Did they have known enemies? A compelling victim, even if flawed, gives the reader someone to care about and root for. Even if the victim hasn't been killed or murdered, who is being bullied or targeted as the victim and why? Where will the story play out? Most stories will have multiple stages, but where will most of the action take place? Will it be a haunted estate house? A corrupt business office? Will it be on the streets in a cityscape? How does the setting influence the mood and the unfolding of the mystery? For example: If it's a gothic novel, you will want a large estate house or a monastery, a place that has secret rooms, tunnels, or has a long history with lots of secrets. If it's a urban thriller, you will need several stages in a city scape. If it's a psychological thriller, it may need at least a mental institution. Think of yourself as a location scout for a movie: What interesting places can most of the drama take place?
Where will the story play out? Most stories will have multiple stages, but where will most of the action take place? Will it be a haunted estate house? A corrupt business office? Will it be on the streets in a cityscape? How does the setting influence the mood and the unfolding of the mystery? For example: If it's a gothic novel, you will want a large estate house or a monastery, a place that has secret rooms, tunnels, or has a long history with lots of secrets. If it's a urban thriller, you will need several stages in a city scape. If it's a psychological thriller, it may need at least a mental institution. Think of yourself as a location scout for a movie: What interesting places can most of the drama take place? Choose a location that not only serves as a backdrop or a stage for the events to take place but which can become its own character. What secrets does the location harbor? Who lived in the historic mansion in another era? Will you need a remote island somewhere to have a closed-door mystery? In a city scape, the backdrop may be about about the certain era, or just a gritty story, or a surreal story. In a mystery drama, what happened in the main family that started all the secrecy? What sin has been passed down through the generations? What corporate setting do you need to show back-door deals or money laundering? What setting can you choose that will enhance the story?
Choose a location that not only serves as a backdrop or a stage for the events to take place but which can become its own character. What secrets does the location harbor? Who lived in the historic mansion in another era? Will you need a remote island somewhere to have a closed-door mystery? In a city scape, the backdrop may be about about the certain era, or just a gritty story, or a surreal story. In a mystery drama, what happened in the main family that started all the secrecy? What sin has been passed down through the generations? What corporate setting do you need to show back-door deals or money laundering? What setting can you choose that will enhance the story?
 Will the story be set in a specific time period? Will it be a general contemporary book that won't reference any specific time period at all? Or will it be specifically cast in an era or time period that will require research?
Will the story be set in a specific time period? Will it be a general contemporary book that won't reference any specific time period at all? Or will it be specifically cast in an era or time period that will require research? There are many blog posts and videos on the internet about how to write a novel. Much of the advice is general in nature and only broad-stroke tips. This video seeks to go one step further and open my last book, which is still being proofread in Layer 8, and show a work-flow demonstration.
There are many blog posts and videos on the internet about how to write a novel. Much of the advice is general in nature and only broad-stroke tips. This video seeks to go one step further and open my last book, which is still being proofread in Layer 8, and show a work-flow demonstration. I am in the process of finishing my 14th novel. I started out like many of you as a self-taught author who took in unorganized, uncurricularized information and had to make sense of it all. I devised this 8 Layer system to try to write a novel as efficiently as was possible. I offer it to you for whatever weight you wish to give it.
I am in the process of finishing my 14th novel. I started out like many of you as a self-taught author who took in unorganized, uncurricularized information and had to make sense of it all. I devised this 8 Layer system to try to write a novel as efficiently as was possible. I offer it to you for whatever weight you wish to give it. In a mystery, crime novel, or thriller, the clues and their revelations need to be planned so the story clues can remain disjointed in the beginning, but then slowly come together like a jigsaw puzzle. This keeps the reader guessing -- which is part of the mystery readers' enjoyment.
In a mystery, crime novel, or thriller, the clues and their revelations need to be planned so the story clues can remain disjointed in the beginning, but then slowly come together like a jigsaw puzzle. This keeps the reader guessing -- which is part of the mystery readers' enjoyment.
 1. Who is the Ghost? Why has the Ghost arisen? Why is the Person not Resting in Peace? What is the Ghost's purpose for appearing? This is the backstory that will be dropped like breadcrumbs throughout the storyline. (Ghost-Story.png)
1. Who is the Ghost? Why has the Ghost arisen? Why is the Person not Resting in Peace? What is the Ghost's purpose for appearing? This is the backstory that will be dropped like breadcrumbs throughout the storyline. (Ghost-Story.png) 1. What is it about the house that's creepy?
1. What is it about the house that's creepy?
 It may help to think of yourself as more of a Town Crier.
It may help to think of yourself as more of a Town Crier. 1. Using the read aloud feature in Microsoft Word, I read the book aloud as I read along with it. This gives you an idea of how the book will sound in the reader's mind.
1. Using the read aloud feature in Microsoft Word, I read the book aloud as I read along with it. This gives you an idea of how the book will sound in the reader's mind. In Layer 8, I do a read-back. In Microsoft Word, I use the Read-Aloud feature that is contained on the Review Tab. By listening to the book read aloud by someone else, it doesn't skip over mistakes like I do as the author. By the time I'm finished with Layer 7, I've read and reread this book too many times to trust my eyes to spot every error.
In Layer 8, I do a read-back. In Microsoft Word, I use the Read-Aloud feature that is contained on the Review Tab. By listening to the book read aloud by someone else, it doesn't skip over mistakes like I do as the author. By the time I'm finished with Layer 7, I've read and reread this book too many times to trust my eyes to spot every error.
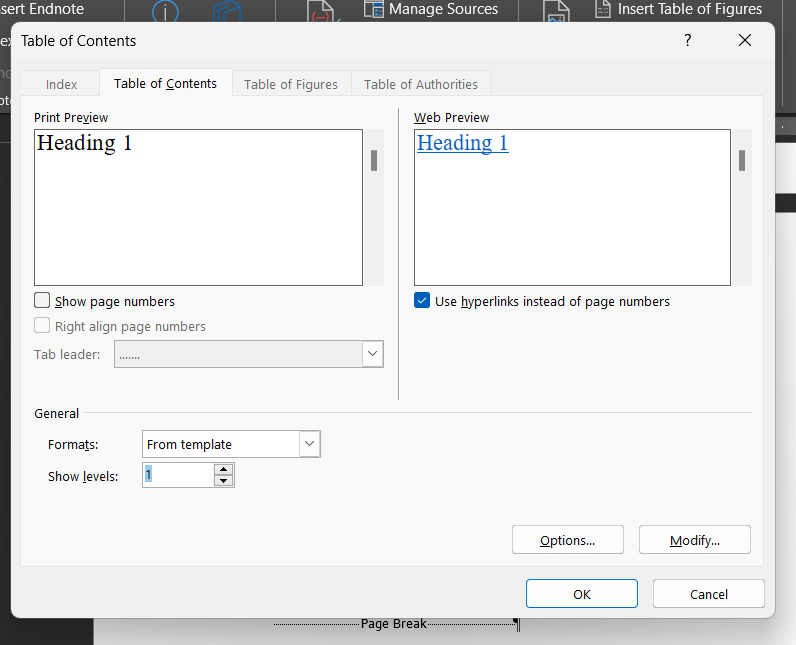
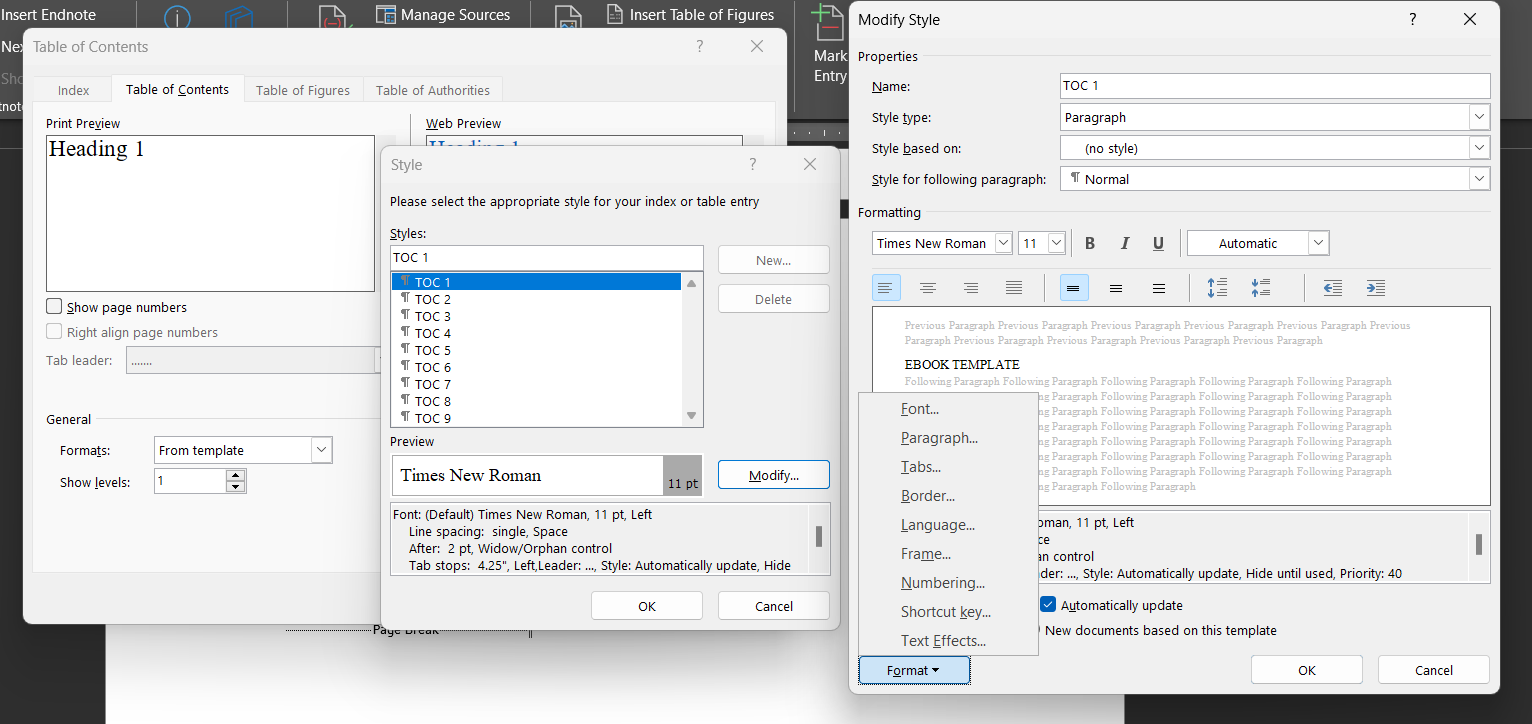
 We compiled the novel into a Word document and named it "Manuscript from Scrivener". That's where we now pick up with Layer 7.
We compiled the novel into a Word document and named it "Manuscript from Scrivener". That's where we now pick up with Layer 7. Layer 6 is the first true proofreading. In Layer 5, I proofread to make sure the story flowed without interruption from scene to scene. My focus was on making sure the story flowed from scene to scene, without any big unexplained time gaps, or location mistakes, etc.
Layer 6 is the first true proofreading. In Layer 5, I proofread to make sure the story flowed without interruption from scene to scene. My focus was on making sure the story flowed from scene to scene, without any big unexplained time gaps, or location mistakes, etc.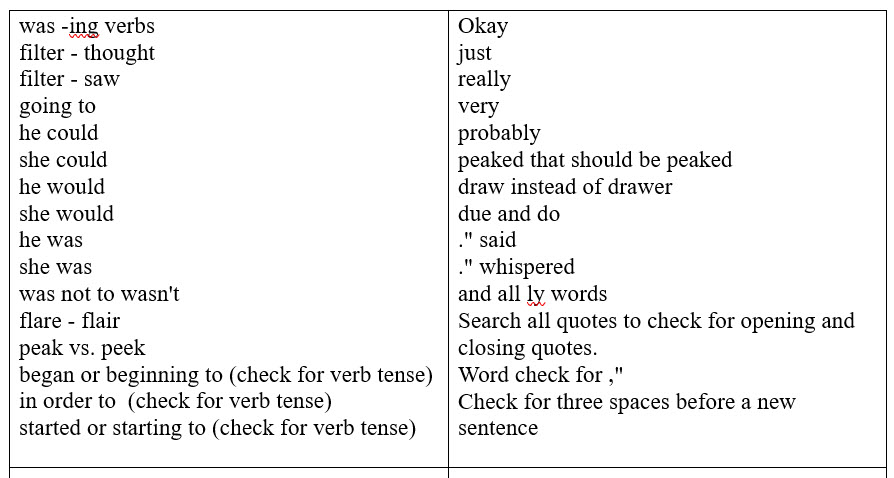
 Once you are finished with Layer 6, Click on File => Compile
Once you are finished with Layer 6, Click on File => Compile Although I follow a detailed outline of the story before I even start writing, each novel presents its own issues and/or problems. In this novel, I had several timelines I had to keep straight.
Although I follow a detailed outline of the story before I even start writing, each novel presents its own issues and/or problems. In this novel, I had several timelines I had to keep straight.


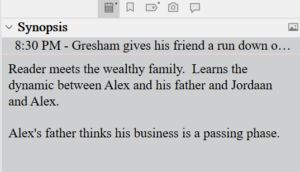 The second thing I do in Layer 5 is to fill out the Synopsis section. This section is in the upper right-hand side of the Scrivener platform.
The second thing I do in Layer 5 is to fill out the Synopsis section. This section is in the upper right-hand side of the Scrivener platform.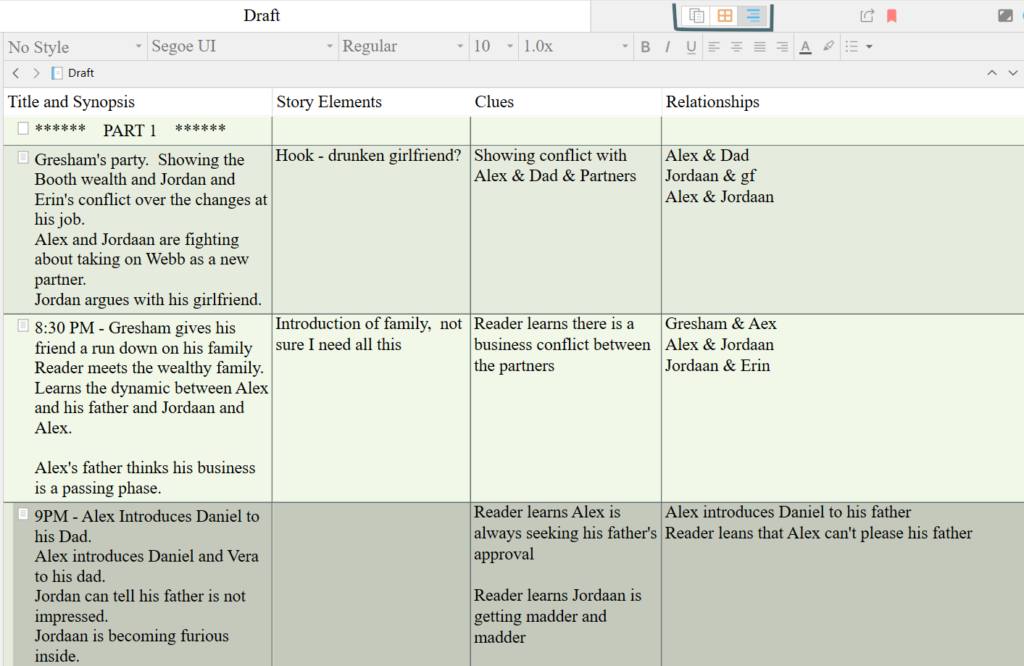
 Now, because I had to kind of abandon the full subplot in Layer 4, I will be finishing the subplot while I'm doing the descriptions and the synopsis box. Once I'm done with this layer, then I'll be back to discuss what happens in Layer 6!
Now, because I had to kind of abandon the full subplot in Layer 4, I will be finishing the subplot while I'm doing the descriptions and the synopsis box. Once I'm done with this layer, then I'll be back to discuss what happens in Layer 6!